英国留学热门专业essay之 企业组织文化 Organizational Culture
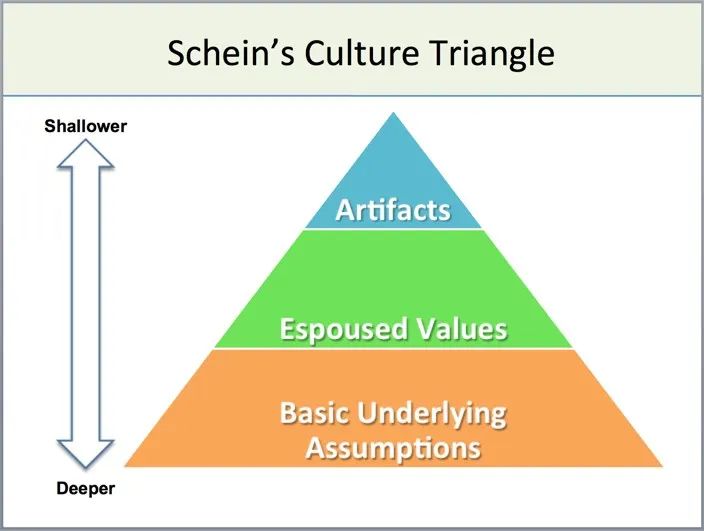
企业文化 是企业 在长期 生存 与发展 过程 中逐渐 形成 的一种 独特 的文化 形象 ,它由价值观念 、信仰 、礼仪 、象征 、执行 方式 等构成 。企业文化 为大多数 企业 成员 所认同 和遵守 。麻省理工 大学 斯隆商学院 管理 教授 EdgarSch ein 将组织文化 划分 为三个 层次 :1)人造 产品 (物理 形态 层次 );2)信念 和价值 ;3)隐含 的假设 和价值 。英国论文代写了解一下?
尽管 组织文化 听起来是一个乏味 而模糊 的概念 ,但它在现代 管理 中却是 一个 非常 重要 的概念 ,只要 是选修 管理课程 的留学生 ,就基本 不能 绕开 这一 理论 。
尽管 有些 枯燥乏味 ,但为了 获得 毕业证书 ,我们 必须 克服困难 。
这是 个令人 心烦 的问题 ,今天 我们 就来聊聊 这一 话题 ,并给大家 介绍 一个 关于 Organizational Culture 的范例 ,希望 能够 给那些 正在 为essay感到 烦恼 的同学们 提供 一些 写作思路。
好了 ,开始吧 !
1. What is organizational culture and how can it be cultivated?
Organizational culture is the ideology, moral fashion, management method and code of conduct recognized, accepted and observed by organization members gradually formed in the long-term development process. Different organizations have different organizational cultures, which embody the uniqueideas of organizations. An organization’s culture is different in various periods.
Organizational culture can improve the motivation of sustainable development and the competitiveness of an organization. Through a lot of research on this issue, it can be observed that there are many factors influencing the generation and transmission of organizational culture. A leader of an organization has the most important influence on the organizational culture.
Edgar Schein once claimed that creating and disseminating organizational culture is an important responsibility of leaders. The relationship between leaders and organizational members also profoundly affects the content of organizational culture. It can be said that team leaders have an important influence on the generation of organizational culture.
The development of organization culture and organization itself advance and retreat together. Besides, they are also interconnected. The development process of organizational culture includes two stages: the initial establishment stage and the later development stage.
This is divided according to the establishment and development process of the organization. This paper will delve into the role of organizational leaders in different stages of organizational culture development.
There are many definitions of leadership and leader. According to statistics, there are more than 350 definitions of “leadership” in the world. There are more than 160 definitions of “leader”. However, this does not mean that “leadership” and “leader” are arbitrary and subjective concepts.
This is the result of research from different disciplines such as politics, histology, management and psychology. Peters said, “leadership means vision. It means love, trust, obsession, persistence, guidance, and many other things. Leaders usually have such characteristics: tireless energy, incredible vision and irresistible persuasion. In addition, confidence, risk taking, initiative and decisiveness are also the characteristics of a leader.
With the development of modern leadership science, a series of systematic discussions about the responsibilities of leaders are put forward from the perspective of disciplines. This should begin with the understanding of “leadership”. Warren Bennis believes that leadership is about “creating and living your dreams.” One person triggers a group to pursue a goal that the leader or organization shares.
According to John Cote’s research, leadership should be defined in the following three meanings: 1) Unite the masses and form an alliance; 2) Reach a consensus on the long-term goal and devote themselves to the realization of this goal; 3) Inspire and encourage, motivate followers’ enthusiasm for work and creation, and overcome obstacles.
In this sense, there are three basic responsibilities of a leader: 1) Propose strategies; 2) Form alliances; 3) Motivate. John Gardner breaks it down even further, proposing four tasks that are important to a leader: 1) Set goals; 2) Determine value; 3) Motivate action; 4) Learn to manage.
Therefore, we can define the connotation of a leader in this way: a leader is to organize a strong human resource system through leadership activities and influence an organized group to set goals. Finally, the leader leads the members of the organization to achieve goals. They are attracted to the characteristics of the leader and follow the leader. These qualities include character, knowledge, ability, faith, and so on.
There are two ways to produce a leader. The first is group leadership. This type is widely spread in society. A group is an aggregate of people between an organization and an individual. Group generally refers to a few people, a dozen people’s small units. For example, families are formal groups, parents are natural leaders, and parents guide their children according to their own values and experiences.
For children, therefore, the first act of leadership takes place at home. In the traditional society, the father is the authority and leader of the family life. In modern society, the mother is often the authority on family life, while the father becomes a follower.
Mayo’s hawthorne experiment identified informal groups in formal organizations. Leaders who emerge naturally from informal groups tend to be more authoritative than leaders of formal groups. In social life, political scientists have long recognized the existence of unappointed leaders, such as Gandhi, nightingale, Martin Luther King, etc.
They had tens of thousands of followers before they even had an organization. In this sense, a leader is different from a manager in that a leader can have no organization but must have followers. Managers can have no followers, but they must be organized.
Another type of leader is formally elected or appointed by an organization. This includes the leader of a registered, registered and recognized official organization. Public sector leaders are a prime example. Public sector leaders are different from ordinary organizational leaders. Public sector leaders deliver needed results in an effective, and legal manner.
Organizational culture originates from social culture. It has mixed with the long accumulated culture to form different characteristics. In an organization, the formation of organizational culture is closely related to its leader’s value orientation. In the organization, its culture shows greater inclusiveness, and the harmony and cohesion of the organization will be enhanced.
When the value orientation of an organization is not accepted by the majority of its members, some internal conflicts may occur in the organizational system. Such an organizational culture can hinder the achievement of organizational goals.
In the book Corporate Culture and Leadership, Schein makes a profound exposition of the connotation of organizational culture. He thought that organizational culture can be regarded as the common values of the members within the organization.
Values reflect the content of organizational culture, but they are not the essence of organizational culture. The word “culture” refers to assumptions and beliefs. Therefore, organizational culture is the hypothesis and belief of the members within the organization.
A very useful result comes from these assumptions and beliefs. They explain the organization’s own purpose and environment in a fundamental way. These assumptions and beliefs are learned. Basedon the above discussion, Schein believes that the connotation of organizational culture is as follows: organizational culture is a mode composed of some basic assumptions.
Many research outcomes suggest that any department has its own unique organizational culture. The culture in organization on the public sector, Fisher claims: “the public organization culture is an idea of public service”. It is different from the private sector and the third sector, with different values and code of conduct system.
It reflects and represents the spirit of the public sector organization as a whole, the common standard of values. Although this definition points out the differences between public and private sector organizational cultures, it fails to reflect the dynamics of the generation and development of a culture in organization.
From the perspective of the emergence and function of organizational culture, Schein defined the organizational culture of public sector as the basic assumption that public sector created and discovered in the process of coping with external adaptability and internal integration. This hypothesis is also the organizational values and behavior patterns Shared by the members of the public sector.
Leadership in the public sector is an activity in itself, reflexing the cultural pattern of the organization itself. Organizational culture becomes the “invisible hand” in public sector management, supporting and maintaining the management of public sector. At the same time, it also affects and restricts all aspects of public sector management.
The culture in organization exists inthe development process of public sector management activities. This includes the written rules and the regulations of the organization as well as the ethics and habits of the organization. Its formation is tightly linked to the value orientation of people in the public sector.
Due to its purposes, historical traditions and other reasons, the culture in organization of the government has the following characteristics:
1) It pursues specific goals. Unlike the private sector, the public sector is not profit-driven. Instead, it emphasizes the service features of public satisfaction and compliance. It mainly aims at the improvement of service quality and the relative stability of social order. Especially under the reform strategy of building “service-oriented organization”, the service characteristics of the public sector are more prominent.
2) It focuses on rules and relative stability. The long-established tradition of the public sector advocates a culture characterized by law-based management, consistent power and responsibility, and hierarchical responsibility. The public sector has a more stable organizational culture than the private sector. At the sametime, the public sector also pays more attention to the normative and static. Therefore, its innovation, participation and dynamic adaptability are also relatively inadequate.
3) Its individuality and uniqueness. The historical tradition, environmental atmosphere, leadership style and personnel quality of the public sector are different. Thus, the organizational culture of the public sector also has its own characteristics. It shows the irreplaceable individuality and uniqueness different from other organizations.
2. Leadership influences organizational culture
The generation of the culture in organization is tightly linked to the style of leaders. Since the 1990s, the relationship between leaders and organizational culture has attracted the attention of many scholars.
1) Research on the relationship between leaders and organizational culture: the generation process of the culture in organization is synchronous with the establishment and development process of the team in a certain sense. The essence of an organization or the consistency of a group is made up of common thoughts, feelings and values generated by the same experience and knowledge.
This is what we end up referring to as the “culture” of the group. There can be no culture without a group, and no “group” without a certain level of culture. So, the development of a group and the formation of a culture can be seen as two different aspects of the same period. The creation and culture of a group is the result of the activities of the leaders.
In his book Visionary Leadership, American scholar Sashkin (1993) believes that “the main responsibility of an organizational leader is to clarify, create and obtain the identity of the members of the organization. These include shared cultural identities, moral convictions, norms of change, and goals. Bass (1997) believes that leaders act as creators and facilitate cultural change.
This effect has both negative andpositive effects. Trice and Beyertl (1995) emphasize the importance of maintaining organizational culture as a leader. Edgar Schein, a famous American scholar in this field, made a systematic theoretical discussion on the relationship between leadership and organizational culture in his book Corporate Culture and Leadership (1992).
He describes in detail the role of leaders in creating, sustaining, and transforming organizational cultures. He believes that the founder of an organization is an important source of organizational culture. Therefore, leaders play a leading role in the formation of organizational culture. This is when senior members of an organization communicate values through everyday conversations.
By organizing all kinds of activities and ceremonies, the important values of the enterprise are repeatedly told. The change of senior members of the organization will weaken the competitiveness of the organization and even change its culture. To create the climate for change, leaders trumpet the existence or potential of a crisis.
At the same time, “Don’t assume that culture, like anything else in an organization, is completely manipulated by managers,” Schein stresses. It constrains the manager more than the manager affects it. In his book The Power of Change — The Difference between Leadership and Management, John kotter (1996) made a detailed study on the relationship between organizational cultureand leadership.
“Leadership is as much about culture as management is about structure,” he says. The formation of an organizational culture needs strong leaders. At the same time, only through a certain form of organizational culture, the organization can find a leader with excellent ability.
2) Research on the relationship between different leadership types and different organizational cultures: academics Deanne and Jaap et al. (2001) use the method of multivariate correlation analysis through empirical survey. They look at the correlation between two different types of leadership and four different types of organizational culture.
These four types of organizational cultures are rule-oriented, goal-oriented, support-oriented and innovation-oriented. They conclude that a rule-based and goal-oriented culture is more relevant to transactional leadership. They are more relevant than transformational leaders. A mechanical environment is more likely to produce transactional leadership.
The goals, structure, and processes of the organization are clear. The opposite is true for leaders who are innovative. The organic environment of transformational leadership has higher matching. Organizational goals and structures are fluid. Yet the environment is benign and trusting, and members expect creativity.
Shane Bwen of the university of Nevada has inferred from a number of scholars that transactional and innovative leaders have different characteristics in “strong cultures” and “weak cultures”. This content is mainly as follows: transactional leaders play the role of supervisors in strong cultures and managers in weak cultures.
Transformational leaders show more characteristics in strong cultures and play a leading role in weak cultures. Meanwhile, Parry et al. (2005) study a number of organizations in New Zealand. They think implementing transformational leadership in an innovative culture leads to greater organizational performance.
Recent research has also focused on the impact of charismatic leadership on organizational culture types. Yukl and Howelldane (2013) study the relationship between the environment and the emergence and effectiveness of charismatic leadership in organizations. They conclud that adaptable organizational cultures are characterized by shared values that emphasize innovation and risk-taking.
Charismatic leaders are more likely to be found in adaptable organizational cultures than in less adaptable ones. Therefore, in the research on the relationship between leadership types and organizational culture types, many scholars classify leadership types mainly based on leaders’ behaviors. Most scholars divide leadership behavior into two types: transactional and innovative.
However, many scholars put laissez-faire leadership in the same category. Jason and Sloan (2007) classify leadership as authoritative, authoritative, participatory, democratic, leading and guiding. They point out that “coercive” and “leader” leadership behaviors can have a detrimental effect on the creation of organizational culture.
Through extensive studies, we find that many scholars believe that there is a close relationship between leaders and organizational culture. Many studies have focused on empirical researches of the effectiveness of leaders’ different leadership behaviors in a certain organizational culture environment. Some of their conclusions provide a good definition of the responsibilities of a leader in an organization.
虽然Organizational Culture 和 Organizational Behavior类的课程很枯燥,但是这些基础理论能够为大家将来写case study提供很好的理论基础,只有理解了这些看似无用的大道理才能写出层次丰富并且理论基础扎实的高质量管理类essay。
